Change Storefront Search Results
After familiarizing yourself with the Storefront search features and learning how to analyze Storefront search results, you may want to go a step further and actually change Storefront search results. Specifically, you'll likely want to change which documents match a given search query (matching) and/or how well each document matches the query (relevance).
Search results are created by matching search documents, created by search models, to a search request body, created by a search query object. These are therefore your extension points. To an extent, you can apply changes to these features via administration and configuration, particularly to manipulate a search request body. (Review the documents linked above for coverage of these concepts and a list of relevant administration and configuration.) However, many changes require deeper extension of these features through decoration.
This document provides a specific example of such a change, as well as commentary on how to adapt these ideas to your own use cases.
Example
For the sake of having a concrete example, we'll use the following:
You're developing an application, and the retailer has previously extended the platform to establish the concept of "promo" products. These products are typically shared via email campaigns and other marketing and are not intended to be merchandised within the Storefront. The retailer has therefore opened a change request for you to exclude promo products from all Storefront search results, since most of Workarea's merchandising features are driven by search.
Setup
In order to work on this change request, first set up some test data. While you could do this entirely through automated tests, for the sake of this document we'll set up seeds and work in a development environment, which is more visual.
Let's assume that as part of a previous change request, another developer has already decorated the catalog product model to add a :promo field to all products.
# app/models/workarea/catalog/product.decorator
module Workarea
decorate Catalog::Product do
decorated do
field :promo, type: Boolean, default: false
end
end
end
This developer also extended the Admin to allow administration of this field.
In production environments, a small number of products (usually 5-10 at any given time) will have this flag set to true.
These are the products that must be excluded from search results.
Start by creating some appropriate seed data to test within your development environment.
The following seeds create four products that will match a search for "promo", but only two of the products are actual promo products (i.e. :promo is true).
The seeds also create categories which merchandise all four of the test products.
One of the categories uses product rules to merchandise the products, while the other uses featured products.
# app/seeds/workarea/promo_products_seeds.rb
module Workarea
class PromoProductsSeeds
def perform
puts 'Adding promo products...'
promo_product_ids = []
# create 4 products that match the search query "promo"
# 2 of which are actual promo products that should not display
# in search results
4.times do | i |
promo = i.even?
name = i.even? ? "Promo (do not merchandize)" : "Not Promo"
sku = "promo-test-#{i}"
product = Catalog::Product.create!(
name: name,
variants: [{ sku: sku }],
promo: promo
)
# collect the product IDs to create a category below
promo_product_ids << product.id
# create corresponding pricing to make products displayable
Pricing::Sku.create!(
id: sku,
prices: [{ regular: Faker::Commerce.price.to_m }]
)
end
# create 2 categories which both include all 4 "promo" products
# the first via product rules
# the second via product IDs (featured products)
Catalog::Category.create!(
name: 'Promo Search',
product_rules: [
{ name: 'search', operator: 'equals', value: 'promo' }
]
)
Catalog::Category.create!(
name: 'Promo Featured',
product_ids: promo_product_ids
)
end
end
end
Add the new seeds to your application's configuration:
# config/initializers/seeds.rb
Workarea.config.seeds << 'Workarea::PromoProductsSeeds'
And then run the seeds:
$ bin/rails db:seed
Now the setup is complete. At this point, searching for "promo" returns all 4 test products.
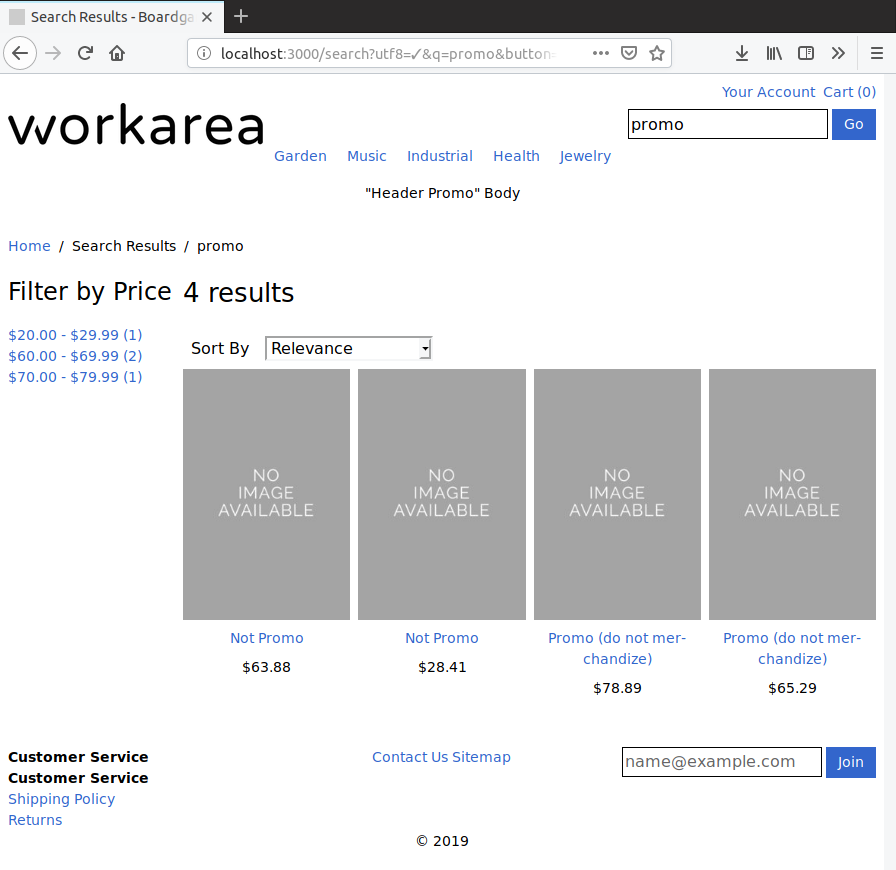
To complete the change request, you must write the code necessary to exclude the promo products from these results. However, the retailer wants to exclude these products from all search results, which includes categories, and product recommendations as well.
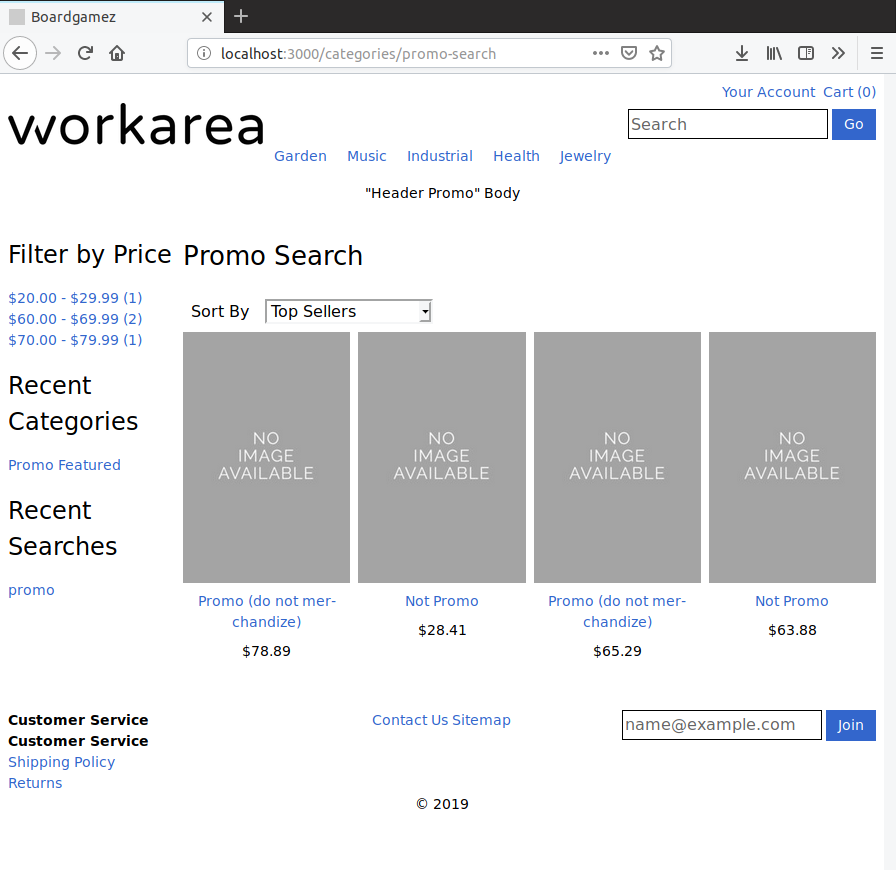
And all four products are included in the "Promo Search" category, which merchandises the products using a product rule:
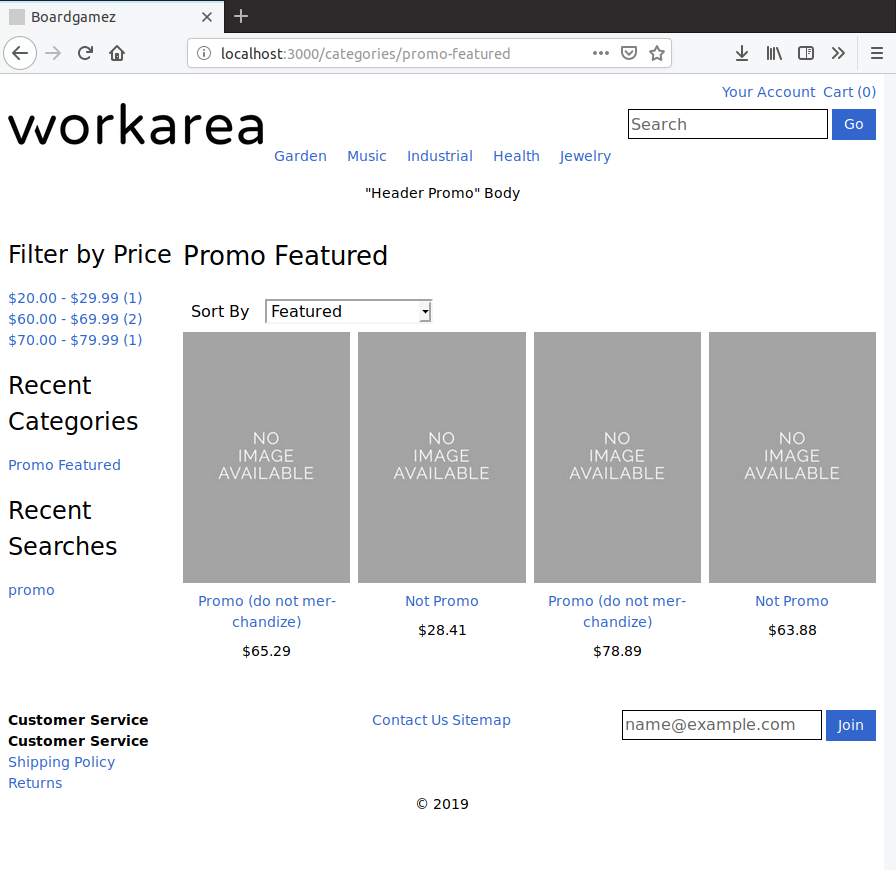
Additionally, the products are all included in the results for the "Promo Featured" category, which merchandises the products using featured products:
Finally, at least one promo product is returned in search results:

(In this doc we won't go into exactly how recommendations work; we'll only cover how to exclude the promo products from the search-based results.)
Changing Search Documents
Most search extensions require changes to the documents and the query.
In the case of our example, we need to add the "promo" flag to product search documents.
While another developer previously extended the catalog product model (for MongoDB documents), the :promo field does not yet exist within the search documents.
To add a field to search documents, identify and decorate the relevant Storefront search model and then re-index the documents.
In the case of our example, the relevant search model is Search::Storefront::Product, to which you must add the :promo field from the catalog model.
An important consideration when adding a field to a search model is the field's mapping (data type).
The promo field in MongoDB is a boolean value.
Search models provide field namespaces to map fields to their correct types.
Review the source for the search model you are decorating to see which namespaces are available.
Looking at the Storefront product search model, there is no boolean namespace, but the keywords namespace is a good choice for the promo field.
Adding the field as keywords.promo will allow you to filter on the field within your search queries and will ensure the field's values are stored as-is, without being analyzed.
# app/models/workarea/search/storefront/product.decorator
module Workarea
decorate Search::Storefront::Product do
def keywords
# add the 'promo' field within the 'keywords' namespace
super.merge(promo: model.promo.to_s)
end
end
end
After applying the changes, re-index the relevant products in the Storefront. In this case, since you're working in a development environment, it's safe to re-index the entire Storefront as a shortcut:
$ bin/rails workarea:search_indexes:storefront
In production environments, modifying the :promo field's value for a given MongoDB document (e.g. through the Admin) will cause the document to be re-indexed into the appropriate search indexes.
Changing Search Queries
After changing the data within the search indexes, you can leverage these changes within your search queries. First determine which search queries you need to change. (Refer to the table in Storefront Search Features, Initialization & Parameters.) Our fictional change request requires changing all queries used within the Storefront.
Ultimately, for each query, you want to change the hash returned by #body, which is the search request body that is sent to Elasticsearch.
Most queries decompose the implementation of #body into several methods, some of which are defined in modules that are shared across queries.
Review the sources for the queries you are changing, and identify the method(s) that represent the portion of the request body you want to change.
The specific methods you change will depend on your use case.
Returning to the promo products example, the goal is to "filter out" all search documents whose keywords.promo field contains the string 'true'.
Three of the four search queries used within the Storefront share a method, product_display_query_clauses, which matches documents based on keyword and other non-analyzed fields.
You can decorate these three queries with a single decorator, modifying that method to include additional clauses to exclude "promo" documents.
# app/queries/workarea/search/product_display_rules.decorator
module Workarea
decorate Search::ProductSearch, Search::CategoryBrowse, Search::RelatedProducts do
def product_display_query_clauses(allow_displayable_when_out_of_stock: true)
result = super
# add a compound query clause to exclude promo products
result << {
bool: {
must_not: {
term: { 'keywords.promo' => true }
}
}
}
result
end
end
end
The example uses the logic "keywords.promo must not contain true" rather than "keywords.promo must contain false" to avoid the need to re-index all search documents for this feature to work.
The chosen logic excludes only those product search documents that have a keywords.promo field and whose value contains 'true'.
Existing search documents without a keywords.promo field will continue to match queries as expected.
Result
Changing the documents and queries as described above has the effect of excluding promo products from all Storefront search results. To verify this manually, re-visit each of the search features, and confirm the two test promo products do not display in the results. In each case, the "Not promo" products continue to match, but the promo products are excluded.
Search results:

Categories:


And recommendations:

Automated Testing
In this doc we used manual testing to confirm the results because it allowed a visual demonstration of the material. However, to avoid regressions, take the time to write automated tests for your changes. This particular example avoids the need to decorate any existing tests, but other use cases may break existing functionality and require test decoration.
See Testing Concepts for coverage of this topic.
Help Us Improve this Doc
Was this helpful? Open a GitHub issue to report a problem with this doc, suggest an improvement, or otherwise provide feedback. Thanks!

